C-View™ Synthesised 2D Imaging
Obtain high quality images while minimising patient radiation and discomfort.

Low-Dose, Highly Accurate Exams
Raise your breast cancer screening performance1-4 with C-View software and instantly generated synthesised 2D images. It not only enhances details and speeds up the analysis, but also reduces radiation dose levels for your patients. C-View 2D images are clinically proven3,5 and FDA approved to diagnostically replace the FFDM images within a tomosynthesis screening exam.
C-View 2D imaging is a purchasable option available on both Selenia® Dimensions® and 3Dimensions™ systems. It is compatible with standard resolution 3D imaging only. It is not compatible with high-resolution 3D imaging.
See More, Do More
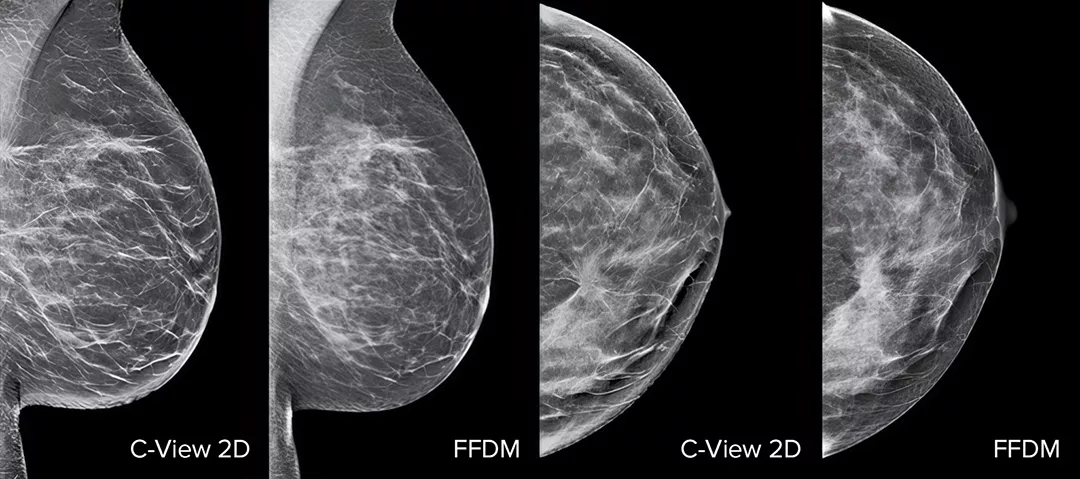
Architectural distortions, mass lesions, and bright spots commonly found in microcalcifications are more visible in the C-View 2D image than on the traditional FFDM 2D images or tomo slices.4,6-9
Superior Performance
Delivers superior clinical performance vs 2D mammography alone for all breast types.4
Reduced Risk
Reduce the risk of retakes5,7 with ultra-fast 3.7-second scans.*10,11
Greater Accuracy
Greater accuracy at a lower dose.**7

Unlock the Advantage of Time
The Breast Health Continuum of Care offers integrated solutions for clinical confidence, workflow efficiency and compassionate patient care. It gives more women, more time in better health.
C-View Synthesised 2D Imaging is part of the Hologic Screening and Diagnosis Solution.
The Proof is in the Details
C-View 2D images are clinically proven3,5 and FDA approved to diagnostically replace the FFDM images within a tomosynthesis screening exam. The images are also a navigational aid to the tomosynthesis slice review. Published studies show that the low dose 3D Mammography exam finds invasive cancer earlier, while also reducing false positive recall rates compared to 2D alone.4,5,7
Architectural distortions, mass lesions, and bright spots commonly found in microcalcifications, are more visible in the C-View 2D image than on the traditional FFDM 2D image or tomo slice.4,6-9

Visit Our Virtual Hospital
Browse our portfolio of Breast Health solutions in 3D. See how you can unlock the advantage of time across the entire Breast Continuum of Care.
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
*Compared to other standard models
** With DBT + synthetic 2D vs DBT + standard 2D
-
Friedewald SM, Rafferty EA, Rose SL, et al. Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography. JAMA. 2014 Jun 25;311(24):2499-507.
-
Rafferty EA, Durand MA, Conant EF, et al. Breast Cancer Screening Using Tomosynthesis and Digital Mammography in Dense and Nondense Breasts. JAMA. 2016;315(16): 1784-6.
-
Zeng B, Yu K, Gao L, Zeng X et al. Breast cancer screening using synthesized two-dimensional mammography: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Elsevier Breast 2021 Oct; 59: 270–278.
-
Bernardi D, Macaskill P, Pellegrini M, et. al. Breast cancer screening with tomosynthesis (3D mammography) with acquired or synthetic 2D mammography compared with 2D mammography alone (STORM-2): a population-based prospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2016 Aug;17(8):1105-13.
-
Skaane P, Bandos A, Eben E, et al. “Two-View Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening with Synthetically Reconstructed Projection Images: Comparison with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis with Full-Field Digital Mammographic Images” Radiology. 2014 Jun; 271(3):655-63.
-
Durand M, Raghu M, Geisel J, et al. “Synthesized 2D Mammography + Tomosynthesis: Can We See Clearly?” (paper presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Chicago, Il, December 2015).
-
Zuckerman SP, Conant EF, Keller BM, et al. Implementation of Synthesized Two-dimensional Mammography in a Population-based Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Screening Program. Radiology. 2016 Dec;281(3):730-736.
-
Zuley M, Guo B, Catullo V, et al. “Comparison of Two-dimensional Synthesized Mammograms versus Original Digital Mammograms Alone and in Combination with Tomosynthesis Images.” Radiology. 2014 Jun;271(3):664-71. Epub 2014 Jan 21.
-
Woo O, Choi G, Shin H, et al. “Comparative Diagnostic Value of Two-dimensional Synthesized Mammogram and Conventional Full-field Digital Mammogram for Evaluation of Breast Cancer” (poster presented at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America, Chicago, Il, December 2015).
-
Rocha Garcia AM., Mera Fernandez D. Breast tomosynthesis: State of the art. Radiologia. 2019;61(4):274-285
-
Lai Y-C, Ray KM, Mainprize JG, et al. Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: Technique and Common Artifacts. Journal of Breast Imaging 2020;2:615-28.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Related Products
2797
Hologic BV, Da Vincilaan 5, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium.
Notified Body number wherever applicable