Aptima® CV/TV assay
Objective, comprehensive and accurate results for Candida vaginitis and Trichomoniasis testing.1

Detect Causes of Infectious Vaginitis
25% of Infectious vaginitis is caused by vulvovaginal candidiasis and 15% by trichomoniasis1. The Aptima CV/TV assay is a Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (NAAT) that helps to detect one of the most common causes of infectious vaginitis: Candida vaginitis (CV) and trichomoniasis (TV). Targets include the Candida species group (C. albicans, C. tropicalis, C. parapsilosis, C. dubliniensis), Candida glabrata and Trichomonas vaginalis.2
Comprehensive, Accurate & Objective Results
The CE-marked Aptima CV/TV assay delivers reliable RT-TMA results for the detection of RNA from microorganisms associated with vulvovaginal candidiasis and trichomoniasis.2
Objective Treatment
An objective tool for the clinician to accurately diagnose and treat patients with a higher sensitivity and specificity than clinician's diagnosis and in-clinic assessment.3
Greater Clarity
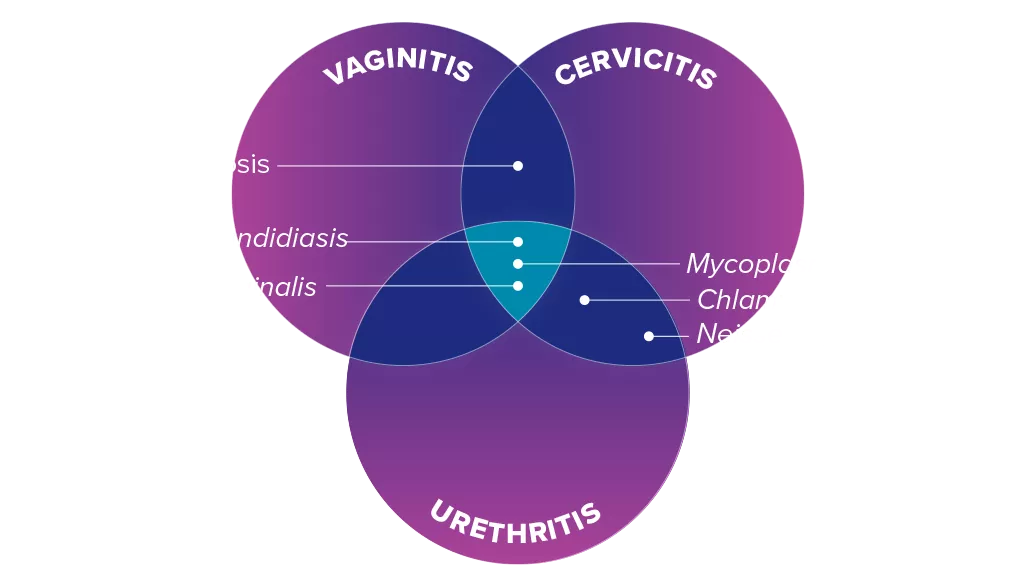
A clinical diagnosis that determines only a single pathogen is likely to be underdiagnosing infections that require different clinical management.4 Overlapping symptoms and co-infections make clinical diagnosis a challenge.5,6
Rapid Results
Time to first result in as little as 2 hrs 41 mins, with five additional results every five minutes.7
Improved Workflow
Benefit form superior workflow, reduced hands-on time and sample volume scalability from running assays on the fully automated Panther® System.8

Simplify & Scale the Future of Diagnostics
The Aptima CV/TV Assay is part of the Hologic Molecular Scalable Solution, a portfolio combining a broad, high-performing assay menu with high-throughput automation. Designed to flexibly scale to meet your needs, from a single patient result to population-level screening.
Excellent Clinical Performance
Qualitative detection of the organisms associated with vulvovaginal candidiasis and trichomoniasis.2
Qualitative detection
of Candida species group and Candida glabrata
Targeting rRNA
for sensitive detection of Trichomonas vaginalis
Excellent sensitivity
and specificity for common causes of vaginitis
Overcome the Clinical Challenges of Accurate Diagnosis
Co-infections and overlapping symptoms make clinical diagnosis a challenge.5 Traditional methodologies are subjective and can impact treatment pathways.
Clinical diagnosis alone does not differentiate the common Candida albicans from Candida glabrata, which is present in 7–16% of yeast infections and is azole resistant.9
Image source6
Test Together. Treat Differently.

Avoid Unnecessary Health Complications
Untreated CV and TV infections can lead to an increased risk of complications, including:
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) such as chlamydia, gonorrhoea, HSV and HIV2,10
- Pelvic inflammatory disease and cervicitis2,10
- Pregnancy-related concerns such as premature delivery, low birth weight and pregnancy loss2,10
Up to 30% of women diagnosed with BV were co-infected with Candida species11
Evidence. Insight. Collaboration.
Our education portal improves patient care through excellence in education, communication of clinical and scientific evidence, and partnerships with the healthcare community.
Insights
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 72. Clinical management guidelines for obstetrician-gynaecologists: Vaginitis. Obstet Gynecol 2006 May; 107(5): 1195-1206.
- Aptima CV/TV Assay [package insert] AW-23713-001 Rev. 001., San Diego, CA; Hologic, Inc., 2023
- Schwebke JR, Taylor SN, Ackerman R, et.al. Clinical Validation of the Aptima Bacterial Vaginosis and Aptima Candida/Trichomonas Vaginitis Assays: Results from a Prospective Multicenter Clinical Study. J Clin Microbiol. 2020;58:e01643-19.
- Van der pol B, Daniel G, Kodsi S, et al. Molecular-based Testing for Sexually Transmitted Infections Using Samples Previously Collected for Vaginitis Diagnosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Feb 1; 68(3): 375-381.
- Anderson MR, Klink K, Cohrssen A. Evaluation of vaginal complaints. JAMA. 2004;291(11):1368–79.
- Adapted from Kent H. Epidemiology of Vaginitis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Oct;165(4 Pt 2):1168-76
- Panther/Panther Fusion System Operator's Manual AW-26055-001 Rev. 001 San Diego, CA: Hologic, Inc.; 2022
- Ratnam S, Jang D, Gilchrist J et.al. Workflow and Maintenance Characteristics of Five Automated Laboratory Instruments for the Diagnosis of Sexually Transmitted Infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014;52(7):2299-2304
- Achkar J, and Fries B. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 23(2):253-273, Fidel Clinical Microbiology Reviews. Jan. 1999; Vol 12. No.1.
- Aptima BV Assay [package insert] AW-23712-001 Rev. 1. San Diego, CA: Hologic, Inc.; 2022
- Sobel J, Subramanian C, Foxman B et al. Mixed Vaginitis—More Than Coinfection and With Therapeutic Implications. Current Infectious Disease Reports. 2013; 15:104–108.
Documents
Safety Data Sheets
Package Inserts
Related Products
1434
2797
Hologic BV, Da Vincilaan 5, 1930 Zaventem, Belgium.
Notified Body number wherever applicable